Picture this: You’ve just launched your dream application after months of development. Everything works perfectly—until a hacker finds a tiny vulnerability you missed and brings your entire system to its knees. Sound familiar?
This scenario happens more often than you’d think, and it’s exactly why security testing methodologies have become the backbone of modern software development. Whether you’re a developer, security professional, or tech leader, understanding these methodologies isn’t just nice-to-have knowledge—it’s absolutely critical for protecting your digital assets.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the most effective security testing approaches, explore real-world applications, and help you choose the right methodology for your specific needs. Ready to transform your security posture? Let’s dive in.
What Are Security Testing Methodologies?
Security testing methodologies are systematic approaches used to identify vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and potential threats in software applications, networks, and systems. Think of them as your digital security blueprint—a structured way to probe your defenses before the bad guys do.
These methodologies go beyond simple vulnerability scanning. They encompass everything from penetration testing and ethical hacking to automated security audits and risk assessments. The goal? To create a comprehensive security strategy that protects against both known threats and emerging attack vectors.
The Core Security Testing Methodologies You Need to Know
1. Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
Static Application Security Testing (SAST) is like having a security expert review your code while you write it. This white-box testing approach analyzes source code, bytecode, or compiled code to identify potential security flaws without executing the program.
Key Benefits:
- Catches vulnerabilities early in the development cycle
- Integrates seamlessly with DevOps pipelines
- Provides detailed remediation guidance
- Cost-effective compared to fixing issues in production
Popular SAST tools include Checkmarx, Veracode, and Fortify Static Code Analyzer. These tools excel at finding issues like SQL injection vulnerabilities, cross-site scripting (XSS) flaws, and insecure coding practices.
2. Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
While SAST examines code at rest, Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tests running applications in real-time. It’s the equivalent of a security professional trying to break into your application from the outside—exactly how real attackers would approach it.
DAST tools like Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP, and Acunetix simulate attacks against web applications, APIs, and mobile apps. They’re particularly effective at finding runtime vulnerabilities that might not be apparent in static code analysis.
3. Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST)
Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) combines the best of both worlds, merging SAST and DAST approaches. It works from inside the application during testing, providing real-time feedback on security issues as the application runs.
IAST tools offer several advantages:
- Lower false positive rates compared to DAST
- More comprehensive coverage than SAST alone
- Real-time vulnerability detection
- Better integration with continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines
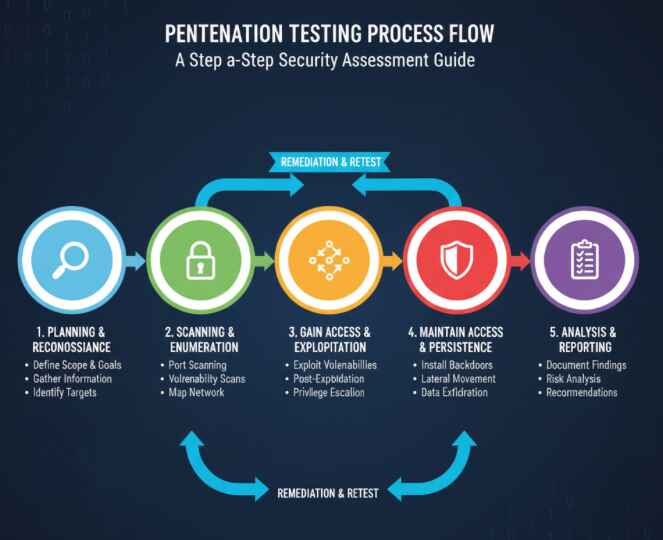
4. Penetration Testing and Ethical Hacking
Penetration testing remains the gold standard for comprehensive security evaluation. This methodology involves skilled security professionals—often called ethical hackers—attempting to exploit vulnerabilities in a controlled environment.
There are three main types of penetration testing:
- Black-box testing: Testers have no prior knowledge of the system
- White-box testing: Complete system knowledge is provided
- Gray-box testing: Limited system information is available
Professional penetration testing typically follows frameworks like OWASP Testing Guide or NIST guidelines, ensuring thorough and standardized assessments.
Specialized Security Testing Approaches
Vulnerability Scanning vs. Penetration Testing
Many organizations confuse vulnerability scanning with penetration testing, but they serve different purposes:
| Aspect | Vulnerability Scanning | Penetration Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Automated tool-based | Manual + automated |
| Depth | Surface-level identification | Deep exploitation |
| Frequency | Continuous/regular | Periodic (quarterly/annually) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Expertise Required | Basic | Advanced |
Fuzz Testing for Edge Cases
Fuzz testing involves feeding applications unexpected, random, or malformed data to identify crashes, memory leaks, or security vulnerabilities. This methodology is particularly effective for finding buffer overflow vulnerabilities and input validation issues.
Modern fuzzing tools can automatically generate thousands of test cases, making them invaluable for discovering edge-case vulnerabilities that traditional testing might miss.
Mobile App Security Testing
With mobile applications dominating the digital landscape, specialized mobile app security testing solutions have become essential. Tools like Mobile Security Framework (MobSF) and platform-specific scanners help identify mobile-specific vulnerabilities like insecure data storage, weak authentication, and reverse engineering risks.
Implementing Security Testing in DevOps Pipelines
Modern development demands continuous security testing strategies integrated directly into CI/CD pipelines. This approach, often called “DevSecOps,” ensures security considerations don’t slow down development velocity.
Key integration points include:
- Pre-commit hooks for basic security checks
- Build-time SAST scanning for code quality
- Deployment-time DAST testing for runtime vulnerabilities
- Production monitoring for ongoing threat detection
Tools like Snyk and Veracode excel at pipeline integration, providing developers with immediate feedback on security issues without disrupting their workflow.
Choosing the Right Security Testing Methodology
Selecting the appropriate methodology depends on several factors:
For Early-Stage Development:
- Start with SAST tools for code-level security
- Implement security testing checklists for developers
- Use automated scanning in CI/CD pipelines
For Production Applications:
- Combine DAST and IAST for comprehensive coverage
- Conduct regular penetration testing
- Implement continuous vulnerability monitoring
For Compliance Requirements:
- Focus on methodologies that support security compliance testing best practices
- Document all testing procedures and results
- Use enterprise-grade tools with detailed reporting capabilities
Measuring Security Testing Effectiveness
How do you know if your security testing is actually working? Key metrics include:
- Vulnerability detection rates across different methodologies
- Time to remediation for identified issues
- False positive rates from automated tools
- Coverage metrics showing tested application components
- Trend analysis of vulnerability types over time
Regular security audits help validate the effectiveness of your testing methodologies and identify areas for improvement.
Emerging Trends in Security Testing
The security testing landscape continues evolving rapidly. Key trends shaping the future include:
- AI-powered security testing for more intelligent threat detection
- Cloud security testing methodologies for multi-cloud environments
- API security testing tools for microservices architectures
- Container security scanning for DevOps workflows
- Quantum-resistant security testing preparing for future threats
Conclusion
Security testing methodologies are no longer optional—they’re fundamental to building trustworthy applications in today’s threat landscape. Whether you choose SAST, DAST, penetration testing, or a combination of approaches, the key is implementing a comprehensive strategy that fits your organization’s needs and risk tolerance.
Remember, security isn’t a destination; it’s a journey. Start with the basics, gradually expand your testing capabilities, and always keep learning about new threats and methodologies.
Ready to strengthen your security posture? Start by evaluating your current testing approaches and identifying gaps. Your future self (and your users) will thank you for the investment in robust security testing.
What’s your experience with security testing methodologies? Share your insights in the comments below, or reach out if you need guidance choosing the right approach for your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between SAST and DAST security testing?
SAST (Static Application Security Testing) analyzes source code without running the application, while DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing) tests running applications in real-time. SAST catches issues early in development, while DAST finds runtime vulnerabilities that might not be apparent in code review.
How often should security testing be performed?
Security testing should be continuous and risk-based. Automated scanning should run with every code commit, comprehensive DAST testing should occur weekly or monthly, and professional penetration testing should happen quarterly or annually, depending on your risk profile and compliance requirements.
What are the most critical vulnerabilities to test for in 2025?
Based on the latest OWASP Top 10, focus on injection flaws, broken authentication, sensitive data exposure, XML external entity (XXE) attacks, broken access control, security misconfiguration, cross-site scripting (XSS), insecure deserialization, known vulnerabilities, and insufficient logging/monitoring.
Can automated tools replace manual penetration testing?
While automated tools are incredibly valuable for continuous monitoring and basic vulnerability detection, they cannot fully replace manual penetration testing. Skilled ethical hackers can identify business logic flaws, complex attack chains, and context-specific vulnerabilities that automated tools might miss.
What’s the best way to integrate security testing into DevOps pipelines?
Start with developer education and security coding guidelines. Implement pre-commit hooks for basic checks, integrate SAST tools into your build process, run DAST scans in staging environments, and use tools like Snyk or Veracode that provide developer-friendly feedback within existing workflows.
How do I prioritize vulnerabilities found during security testing?
Use a risk-based approach considering vulnerability severity (CVSS scores), exploitability, business impact, and regulatory requirements. Focus on critical and high-severity issues first, especially those in internet-facing applications or systems handling sensitive data. Tools like Tenable.io and Qualys provide excellent vulnerability prioritization features.
Sources:
- OWASP Testing Guide: https://owasp.org/www-project-web-security-testing-guide/
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework
- SANS Institute Security Testing Resources: https://www.sans.org/white-papers/