At 3:47 AM on a Tuesday, Sarah’s phone buzzed with an alert that would change everything. As the IT director of a mid-sized marketing firm, she watched in horror as their primary servers went dark—victims of a sophisticated ransomware attack. With no proper disaster recovery planning for information security, her company faced weeks of downtime and potential bankruptcy.
Don’t let Sarah’s nightmare become your reality. In today’s threat landscape, where cyberattacks occur every 39 seconds, having a robust disaster recovery plan isn’t just smart—it’s essential for survival.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through building bulletproof disaster recovery strategies that protect your organization from the worst-case scenarios. You’ll discover the critical components every plan needs, learn industry best practices, and explore the tools that can automate your recovery processes.
Understanding Disaster Recovery in the Cybersecurity Context
Disaster recovery goes beyond simple data backups. It’s a comprehensive strategy that ensures your organization can quickly restore critical operations after any disruptive event—whether that’s a cyberattack, natural disaster, or hardware failure.
Think of your disaster recovery plan (DRP) as a detailed playbook that your team follows when chaos strikes. Just like firefighters train for emergencies, your IT team needs clear procedures to follow when systems go down.
The stakes couldn’t be higher. According to IBM’s latest research, the average cost of a data breach now exceeds $4.45 million, with small businesses often closing permanently after major incidents.
Core Components of Information Security Disaster Recovery
Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis
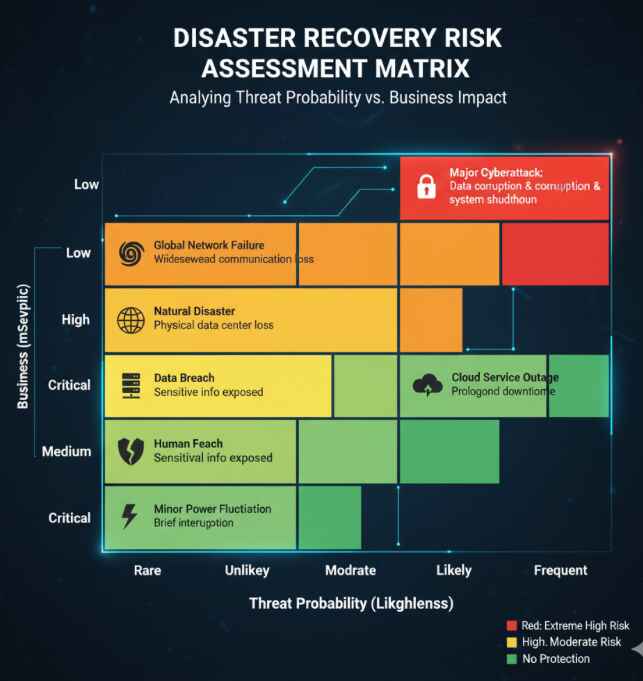
Before building your fortress, you need to know what you’re defending against. A thorough disaster recovery risk assessment identifies potential threats and their likelihood of occurrence.
Key risk categories include:
- Cyberattacks: Ransomware, data breaches, DDoS attacks
- Natural disasters: Floods, earthquakes, fires
- Technology failures: Server crashes, network outages
- Human errors: Accidental deletions, misconfigurations
Defining Recovery Objectives
Here’s where many organizations stumble—they skip the critical step of defining Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
RTO answers: “How quickly must we restore operations?” RPO answers: “How much data can we afford to lose?”
| System Type | Typical RTO | Typical RPO |
|---|---|---|
| Critical business apps | 1-4 hours | 15-30 minutes |
| Email systems | 4-8 hours | 1-2 hours |
| File servers | 8-24 hours | 4-8 hours |
| Archive systems | 24-72 hours | 24 hours |
These objectives drive every other decision in your IT disaster recovery best practices implementation.
Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
Your data backup and recovery strategy forms the backbone of any effective disaster recovery plan. The 3-2-1 backup rule remains the gold standard: three copies of critical data, stored on two different media types, with one copy kept offsite.
However, modern threats like ransomware require more sophisticated approaches. Many organizations now implement “air-gapped” backups—completely isolated copies that malware cannot reach.
I learned this lesson when consulting for a healthcare clinic that discovered their “secure” cloud backups were encrypted along with their primary systems during a ransomware attack. The attackers had compromised their cloud credentials months earlier.
Building Your Disaster Recovery Communication Plan
When disaster strikes, clear communication can mean the difference between controlled recovery and total chaos. Your disaster recovery communication plan should include:
Internal communications:
- Emergency contact trees for IT staff
- Notification procedures for executives
- Employee update mechanisms
- Vendor and supplier contacts
External communications:
- Customer notification templates
- Media response protocols
- Regulatory reporting requirements
- Insurance company contacts
The Role of Automated Runbooks
Manual recovery processes are slow, error-prone, and stressful. Automated runbooks transform your disaster recovery from a manual scramble into a systematic, repeatable process.
These digital playbooks can automatically:
- Detect system failures
- Initiate failover procedures
- Restart critical services in proper sequence
- Notify stakeholders of progress
- Document recovery actions for compliance
Leading organizations report 75% faster recovery times when using automated runbooks compared to manual processes.
Cloud Services and Modern Disaster Recovery
Cloud disaster recovery solutions have revolutionized how organizations approach resilience planning. Instead of maintaining expensive secondary data centers, businesses can leverage cloud infrastructure for rapid failover.
Key advantages of cloud-based DR:
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Faster deployment times
- Automated scaling during incidents
- Geographic distribution options
- Pay-per-use pricing models
However, cloud adoption introduces new complexities around data sovereignty, vendor lock-in, and shared responsibility models that your plan must address.
Addressing Modern Threats: Ransomware Recovery
Ransomware recovery solutions require special consideration in today’s threat landscape. Traditional backup strategies often fail against modern ransomware variants that encrypt backups and delete shadow copies.
Effective ransomware protection includes:
- Immutable backup copies that cannot be modified
- Network segmentation to prevent lateral movement
- Regular testing of backup integrity
- Incident response procedures for crypto-malware
- Legal and regulatory notification requirements
Testing and Maintenance: The Often-Forgotten Elements
A disaster recovery plan is only as good as its last successful test. Yet many organizations create elaborate plans that gather dust until an actual emergency reveals their flaws.
Essential testing approaches:
- Tabletop exercises: Team discussions of hypothetical scenarios
- Partial failovers: Testing individual system recovery
- Full disaster simulations: Complete environment failover tests
- Surprise drills: Unannounced tests to verify real-world readiness
Schedule these tests quarterly for critical systems, and annually for less critical infrastructure. Document results, identify gaps, and update procedures based on lessons learned.
Essential Tools for Disaster Recovery Planning
The right tools can dramatically simplify your disaster recovery implementation and management:
Enterprise Solutions:
- Veeam Backup & Replication for comprehensive virtual environment protection
- Zerto Disaster Recovery for real-time replication and automated failover
- Microsoft Azure Site Recovery for cloud-native disaster recovery
Mid-Market Options:
- Acronis Cyber Protect combining backup with cybersecurity
- Datto SIRIS offering all-in-one business continuity
- Carbonite Server Backup for hybrid cloud protection
Small Business Tools:
- SolarWinds Backup for simple, affordable protection
- Barracuda Backup with built-in ransomware detection
- N-able Backup designed for managed service providers
Choose tools that align with your RTO/RPO objectives and integrate well with your existing infrastructure.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Many industries face specific disaster recovery compliance standards that your plan must address:
- HIPAA for healthcare organizations
- SOX for publicly traded companies
- PCI DSS for payment card processors
- GDPR for organizations handling EU citizen data
These regulations often mandate specific recovery timeframes, data protection measures, and documentation requirements that influence your disaster recovery design.
Conclusion: Building Resilience in an Uncertain World
Disaster recovery planning for information security isn’t just about technology—it’s about ensuring your organization survives and thrives despite inevitable disruptions. The key lies in taking a systematic approach that combines thorough risk assessment, clear objectives, robust testing, and the right tools.
Remember Sarah’s 3:47 AM nightmare? Six months later, after implementing a comprehensive disaster recovery plan, her company faced another cyberattack. This time, automated systems detected the threat, isolated affected systems, and restored operations from clean backups within four hours. The difference? Preparation.
Start building your disaster recovery plan today. Begin with a simple risk assessment, define your recovery objectives, and gradually expand your capabilities. Your future self—and your stakeholders—will thank you when disaster strikes.
What’s your biggest disaster recovery concern? Share your challenges in the comments below, and let’s discuss strategies to address them.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between disaster recovery and business continuity planning?
Disaster recovery focuses specifically on restoring IT systems and data after an incident, while business continuity planencompasses all aspects of maintaining operations during disruptions, including alternative work arrangements, supply chain management, and customer communications. Think of DR as a subset of the broader business continuity strategy.
How often should I test my disaster recovery plan?
Disaster recovery testing frequency depends on system criticality and regulatory requirements. Most experts recommend quarterly testing for mission-critical systems and annual testing for less critical infrastructure. However, any significant infrastructure changes should trigger additional testing to ensure your plan remains effective.
What are the most important metrics to track in disaster recovery?
The two most critical metrics are Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO). RTO measures how quickly you can restore operations, while RPO indicates how much data you can afford to lose. Additional metrics include mean time to recovery (MTTR), backup success rates, and test failure rates.
How does ransomware affect traditional disaster recovery strategies?
Ransomware recovery solutions require special considerations because modern ransomware can encrypt both primary data and traditional backups. Effective protection requires immutable backup copies, network segmentation, regular backup testing, and incident response procedures specifically designed for crypto-malware attacks.
Should small businesses use cloud-based disaster recovery?
Cloud disaster recovery solutions offer significant advantages for small businesses, including lower upfront costs, faster deployment, and reduced complexity compared to traditional secondary data centers. However, consider factors like internet bandwidth, data sovereignty requirements, and monthly operational costs when making your decision.
What role do managed service providers play in disaster recovery?
MSP disaster recovery services can provide expertise and resources that many organizations lack internally. MSPs offer 24/7 monitoring, automated backup management, and rapid response capabilities. This is particularly valuable for small to medium businesses that cannot justify full-time disaster recovery specialists on staff.
Sources: