Last month, I watched a small marketing agency lose three years of client work when their cloud storage got compromised. The owner thought their data was automatically secure just because it lived “in the cloud.” That painful lesson cost them $50,000 in recovery efforts and nearly destroyed their reputation.
How to secure your data in the cloud isn’t just about choosing a reputable provider—it’s about implementing layered security strategies that protect your most valuable digital assets. Whether you’re a small business owner or managing enterprise-level data, understanding cloud data security fundamentals can mean the difference between business continuity and catastrophic loss.
In this guide, you’ll discover proven methods for encrypting sensitive data, implementing zero-trust security models, controlling user access effectively, and selecting the right security tools to create an impenetrable cloud fortress around your information.
Understanding the Cloud Security Landscape
Cloud environments operate differently than traditional on-premise systems, creating unique security challenges that many organizations underestimate. The shared responsibility model means your cloud service provider handles infrastructure security, while you’re responsible for securing your data, applications, and user access.
Think of it like renting an apartment in a secure building. The building owner provides locked doors, security cameras, and guards, but you still need to lock your own apartment door and protect your valuables inside.
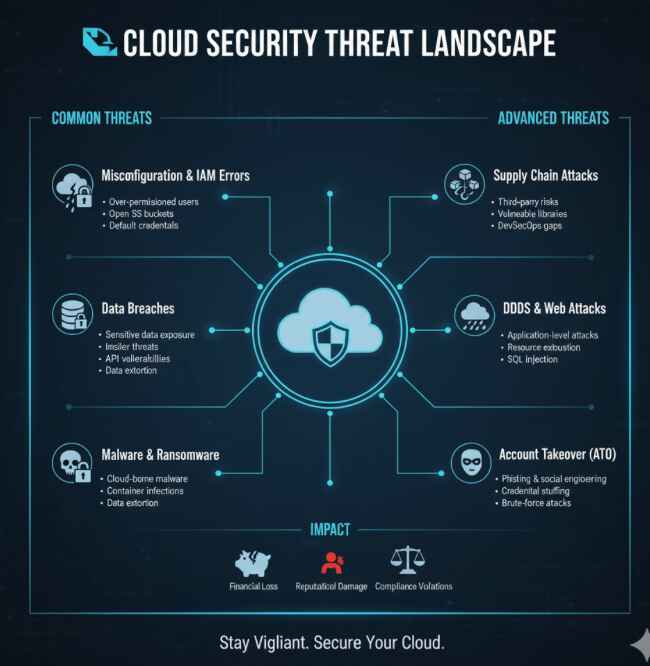
The Real Risks Hiding in Your Cloud
Data breaches in cloud environments typically happen through:
- Misconfigured access permissions (65% of incidents)
- Weak authentication protocols (23% of cases)
- Unencrypted data transmission (12% of breaches)
Essential Cloud Data Security Best Practices
1. Implement Zero Trust Cloud Security Architecture
Zero trust cloud security operates on the principle “never trust, always verify.” Instead of assuming users inside your network are safe, every access request gets authenticated and authorized continuously.
I’ve seen this approach stop insider threats that traditional perimeter security missed completely. One client caught an employee attempting to download customer databases at 2 AM—something that would’ve been nearly impossible to detect with older security models.
Key zero trust components include:
- Continuous authentication for all users and devices
- Micro-segmentation of cloud resources
- Least privilege access policies
- Real-time risk assessment for every transaction
2. Master Cloud Data Encryption Strategies
Cloud data encryption should happen at three critical stages: data at rest, data in transit, and data in use. Many organizations only encrypt stored data, leaving massive vulnerabilities during transmission and processing.
Here’s what comprehensive encryption looks like:
| Encryption Type | What It Protects | Recommended Method |
|---|---|---|
| At Rest | Stored files and databases | AES-256 encryption |
| In Transit | Data moving between systems | TLS 1.3 protocols |
| In Use | Data being processed | Homomorphic encryption |
3. Establish Robust Cloud Access Control
Cloud access control goes beyond simple username/password combinations. Modern threats require multi-layered authentication that adapts to user behavior and risk levels.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be non-negotiable for any cloud access. But don’t stop there—implement just-in-time (JIT) access for administrative privileges. This means users only receive elevated permissions when needed for specific tasks, then access automatically expires.
4. Deploy Data Loss Prevention Cloud Solutions
Data loss prevention cloud tools act like intelligent security guards, monitoring every piece of information leaving your environment. These systems can identify sensitive data patterns and block unauthorized transfers before they happen.
The best cloud-native data loss prevention (DLP) solutions use machine learning to understand normal data flow patterns, making them incredibly effective at spotting anomalies that indicate potential breaches.
Advanced Cloud Security Posture Management
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Cloud security posture management requires constant vigilance. Automated monitoring tools can track configuration changes, access patterns, and potential threats 24/7, something that’s impossible with manual oversight.
Effective cloud incident response protocols should include:
- Automated threat detection triggers
- Pre-defined escalation procedures
- Rapid containment strategies
- Recovery and forensics processes
Selecting Trustworthy Cloud Service Providers
Your cloud service provider security evaluation should examine more than just marketing claims. Look for providers with:
- SOC 2 Type II certifications
- ISO 27001 compliance
- Regular third-party security audits
- Transparent incident reporting history
Top Cloud Security Tools for 2025
Based on current market analysis, here are the most effective solutions for comprehensive cloud data protection:
Enterprise-Level Platforms:
- Microsoft Azure Security Center – Unified security management with advanced threat protection
- AWS Security Hub – Centralized security posture management across AWS environments
- Prisma Cloud by Palo Alto Networks – Multi-cloud security with AI-driven threat detection
Specialized Security Solutions:
- Netskope Cloud Security Platform – Advanced CASB with real-time data protection
- Thales CipherTrust Cloud Key Manager – Centralized encryption key management
- Vectra AI – Machine learning-powered threat detection
The right combination depends on your specific cloud environment, data sensitivity levels, and compliance requirements.
Ensuring Compliance and Data Privacy
Cloud compliance standards vary by industry, but most organizations need to address GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, or SOX requirements. The key is understanding how these regulations apply to cloud-stored data and implementing appropriate safeguards.
Protecting sensitive data in multi-tenant cloud environments requires additional layers of isolation and encryption. Virtual private clouds (VPCs) and dedicated tenancy options provide enhanced separation from other customers’ data.
Conclusion
Securing your data in the cloud isn’t a one-time setup—it’s an ongoing process that evolves with new threats and technologies. The marketing agency I mentioned earlier? They’ve since implemented every strategy in this guide and haven’t had a single security incident in over two years.
Start with the fundamentals: strong encryption, zero-trust principles, and robust access controls. Then layer on advanced monitoring and specialized security tools based on your specific needs. Remember, the cost of prevention is always less than the price of recovery.
Ready to fortify your cloud security? Share this guide with your team and start implementing these essential protections today. What’s your biggest cloud security concern? Drop a comment below—I’d love to help you tackle specific challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the shared responsibility model in cloud security?
The shared responsibility model divides security duties between cloud providers and customers. Providers secure the infrastructure, while customers protect their data, applications, and user access. Think of it like living in a secure apartment building—the landlord provides building security, but you secure your own unit.
How often should cloud data security policies be updated?
Cloud security policies should be reviewed quarterly and updated whenever you add new services, change compliance requirements, or experience security incidents. The cloud landscape evolves rapidly, so static policies quickly become obsolete.
What role does machine learning play in cloud data security?
Machine learning for cloud security excels at pattern recognition and anomaly detection. These systems learn normal behavior patterns and can instantly identify suspicious activities that human administrators might miss, like unusual data access patterns or unexpected file transfers.
How can I ensure data integrity in cloud environments?
Cloud data integrity verification requires implementing checksums, digital signatures, and regular audit trails. Use cryptographic hashing to detect unauthorized changes and maintain detailed logs of all data modifications with timestamp and user information.
What are the best practices for backup and disaster recovery in the cloud?
Backup and disaster recovery cloud best practices include the 3-2-1 rule: maintain three copies of critical data, store them on two different media types, and keep one copy off-site. Automate backup processes and regularly test recovery procedures to ensure they work when needed.
How do I balance cloud accessibility with security requirements?
Balancing accessibility and security requires implementing adaptive access controls that adjust based on user location, device trust level, and data sensitivity. Use single sign-on (SSO) for convenience while maintaining strong authentication for sensitive resources.
Sources: