The Million-Dollar Question Every CISO Faces
Picture this: You’re sitting in a boardroom, and the CEO asks, “Are we compliant with global security standards?” The room falls silent. Your palms get sweaty. You know you have some security measures in place, but which standards actually apply to your business? And more importantly, are you meeting them?
This exact scenario played out at a Fortune 500 company I consulted for last year. They thought they were “secure enough” until a compliance audit revealed gaps that could have cost them millions in fines and reputation damage. That’s when they realized the critical importance of understanding global information security standards explained in plain English.
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, navigating the maze of information security standards isn’t just about checking boxes – it’s about building a resilient foundation that protects your organization, customers, and stakeholders. This guide will demystify the most important standards, show you how they work together, and help you determine which ones matter most for your organization.
What Are Global Information Security Standards?
Think of information security standards as the universal language of cybersecurity. Just like how electrical outlets have different standards worldwide, information security has established frameworks that organizations use to protect data and systems consistently across borders.
These standards serve as blueprints, providing structured approaches to:
- Identifying and managing security risks
- Implementing appropriate security controls
- Demonstrating compliance to regulators and customers
- Building trust with stakeholders and partners
- Creating consistency across global operations
The beauty of these standards lies in their universality – a company compliant with ISO 27001 in Tokyo can confidently do business with a partner in New York, knowing they both speak the same security language.
The Big Players: Essential Global Security Standards
ISO/IEC 27001: The Gold Standard of Information Security
ISO 27001 remains the crown jewel of information security standards worldwide. This comprehensive framework focuses on establishing, implementing, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
What makes ISO 27001 special? It’s outcome-focused rather than prescriptive. Instead of telling you exactly what security tools to buy, it guides you through:
- Risk assessment and treatment processes
- Security control implementation
- Regular monitoring and review cycles
- Continuous improvement methodologies
I’ve watched organizations transform their security posture through ISO 27001 implementation. One mid-sized software company reduced their security incidents by 78% within the first year of certification.
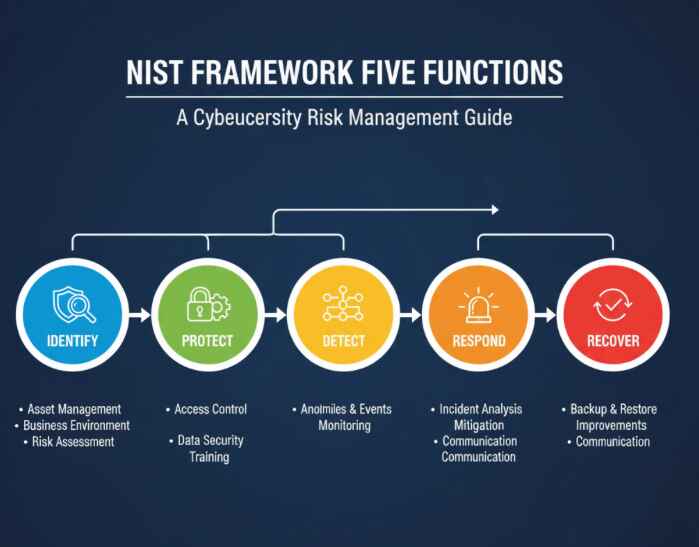
NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The American Approach
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework takes a different but equally effective approach. Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, this framework organizes security activities into five core functions:
- Identify: Understanding your assets and risks
- Protect: Implementing appropriate safeguards
- Detect: Finding cybersecurity events quickly
- Respond: Taking action when incidents occur
- Recover: Restoring capabilities after incidents
Unlike ISO 27001’s certification process, NIST CSF implementation focuses on practical, flexible guidance that organizations can tailor to their specific needs and risk profiles.
Data Protection Standards: Navigating the Privacy Landscape
GDPR: Europe’s Privacy Revolution
GDPR data protection fundamentally changed how organizations worldwide handle personal data. Even if you’re not based in Europe, you likely need GDPR compliance if you process EU citizens’ data.
Key GDPR requirements include:
- Data minimization: Collect only necessary information
- Purpose limitation: Use data only for stated purposes
- Consent management: Clear, withdrawable consent mechanisms
- Data breach reporting: 72-hour notification requirements
- Right to be forgotten: Data deletion upon request
The financial impact is real – GDPR fines exceeded €1.2 billion in 2023 alone. But beyond avoiding penalties, GDPR compliance builds customer trust and competitive advantage.
Industry-Specific Standards: Tailored Protection
PCI DSS compliance protects payment card data through specific technical and operational requirements. Any organization that stores, processes, or transmits credit card information must comply with these standards.
Similarly, HIPAA security rules govern healthcare data protection in the United States, establishing administrative, physical, and technical safeguards for protected health information.
Governance and Risk Management Frameworks
SOC 2: Trust Through Transparency
SOC 2 requirements focus on five trust service criteria: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. This standard is particularly important for technology service providers and cloud companies.
The SOC 2 audit process provides customers with detailed reports about your security controls, creating transparency that builds business relationships and enables contract negotiations.
COBIT: IT Governance Excellence
COBIT governance bridges the gap between business requirements, IT processes, and security controls. This framework helps organizations align IT initiatives with business objectives while maintaining appropriate risk management.
| Standard | Primary Focus | Best For | Certification Available |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 27001 | ISMS Management | All Organizations | Yes |
| NIST CSF | Risk Management | US Organizations | No (Self-Assessment) |
| GDPR | Data Privacy | EU Data Processors | No (Compliance Required) |
| PCI DSS | Payment Security | Card Data Handlers | Yes |
| SOC 2 | Service Provider Trust | Cloud/Tech Companies | Yes |
| COBIT | IT Governance | Large Enterprises | Yes |
Implementation Strategy: Making Standards Work for You
Starting Your Compliance Journey
The key to successful global information security compliance lies in strategic planning. Don’t try to tackle everything at once – prioritize based on your business needs, regulatory requirements, and risk profile.
Step 1: Assessment and Gap Analysis Begin with a comprehensive review of your current security posture against relevant standards. I recommend using automated tools like RSA Archer or MetricStream GRC Platform to identify gaps efficiently.
Step 2: Risk-Based Prioritization Not all requirements carry equal risk. Focus first on controls that address your highest-risk areas. For example, if you handle payment data, PCI DSS compliance should take priority over other frameworks.
Step 3: Implementation Roadmap Create a realistic timeline that balances security improvement with business continuity. Most organizations find success with 12-18 month implementation cycles for major standards like ISO 27001.
Leveraging Technology for Compliance
Modern GRC platforms significantly simplify standards management. Tools like ServiceNow GRC and LogicManager GRC automate compliance tracking, audit preparation, and risk assessment processes.
For smaller organizations, platforms like Secureframe provide automated compliance solutions specifically designed for ISO 27001 and SOC 2 certification, reducing the traditional cost and complexity barriers.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
The Resource Reality Check
“We don’t have the budget for compliance” is the most common objection I hear. However, the cost of non-compliance almost always exceeds implementation costs. Consider these approaches:
- Start with frameworks, not certifications: Implement standard practices before pursuing formal certification
- Leverage existing tools: Most organizations already have security tools that support compliance
- Focus on high-impact controls: Prioritize controls that provide both security and compliance benefits
Avoiding Compliance Theater
The biggest mistake organizations make is treating compliance as a checklist exercise. Real security comes from understanding the why behind each requirement and implementing controls that actually reduce risk.
Emerging Trends in Global Security Standards
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Standards are evolving to address artificial intelligence risks and opportunities. The EU’s upcoming AI Act will likely influence global AI governance approaches, while existing frameworks incorporate AI-specific risk considerations.
Cloud-First Approaches
Traditional standards are adapting to cloud-native architectures. New guidance addresses container security, serverless computing, and multi-cloud governance challenges.
Supply Chain Security
Recent high-profile attacks have elevated supply chain security requirements across multiple standards. Expect increased focus on third-party risk management and software bill of materials (SBOM) requirements.
Selecting the Right Standards for Your Organization
The question isn’t whether you need security standards – it’s which ones align with your business objectives and risk profile. Consider these factors:
Regulatory Requirements: Some standards are mandatory based on your industry or geographic location Business Relationships: Many customers and partners require specific certifications Risk Profile: Your threat landscape should influence standard selection Organizational Maturity: Start with foundational standards before pursuing advanced frameworks
Building a Culture of Compliance
Successful standards implementation requires more than technology and processes – it demands cultural change. Organizations that excel at compliance treat security standards as enablers of business success rather than bureaucratic obstacles.
Training and Awareness: Regular information security training requirements ensure all employees understand their role in maintaining compliance Executive Support: Leadership commitment to compliance creates organizational accountability Continuous Improvement: Standards compliance is an ongoing journey, not a destination
Measuring Success: KPIs for Standards Compliance
Track these key metrics to gauge your compliance program effectiveness:
- Audit findings trends (should decrease over time)
- Incident response time improvements
- Risk assessment completion rates
- Control effectiveness measurements
- Business impact metrics (customer trust, contract wins)
The Global Perspective: Cross-Border Considerations
Cross-border data protection standards create complex compliance landscapes. Organizations operating internationally must navigate multiple regulatory regimes while maintaining operational efficiency.
Key considerations include:
- Data residency requirements
- Cross-border data transfer mechanisms
- Jurisdictional conflict resolution
- Harmonized control implementation
Future-Proofing Your Compliance Program
Evolving cybersecurity standards 2025 will likely address quantum computing threats, enhanced privacy requirements, and emerging technology risks. Build flexibility into your compliance program to adapt to changing requirements.
Stay ahead by:
- Participating in industry working groups
- Monitoring regulatory development
- Investing in adaptable security architectures
- Building internal expertise and external partnerships
Conclusion
Understanding global information security standards explained isn’t just about avoiding penalties or passing audits – it’s about building organizational resilience in an increasingly complex threat landscape. The companies that thrive are those that view compliance as a strategic advantage rather than a necessary burden.
Whether you’re just beginning your compliance journey or optimizing existing programs, remember that standards provide proven frameworks for managing risk and building trust. The investment you make today in understanding and implementing these standards will pay dividends in reduced risk, increased customer confidence, and competitive advantage.
Ready to dive deeper into security standards implementation? Share your biggest compliance challenge in the comments below, or connect with our team to discuss how these frameworks might work for your specific situation. Your journey to robust information security starts with understanding the standards that matter most to your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do organizations choose the right information security standard for their needs?
The selection process should start with a global information security compliance assessment based on three key factors: regulatory requirements (what laws mandate), business needs (what customers and partners require), and risk profile (what threats you face). For example, healthcare organizations typically prioritize HIPAA compliance, while payment processors focus on PCI DSS. Many organizations adopt ISO 27001 as a foundational standard because it provides comprehensive coverage that often satisfies multiple compliance requirements simultaneously.
What’s the difference between a security standard and a security framework?
A security framework (like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework) provides high-level guidance and principles for organizing security activities, while security standards (like ISO 27001) offer specific requirements and criteria that can be audited and certified. Frameworks are typically more flexible and adaptable, allowing organizations to customize their approach, whereas standards provide measurable compliance requirements with clear pass/fail criteria.
How often should organizations conduct security audits for compliance with information security standards?
Most information security standards require annual external audits for certification maintenance, but internal audit frequency varies by standard and risk level. ISO 27001 requires management reviews at least annually, while high-risk environments may benefit from quarterly internal assessments. SOC 2 requirements typically involve continuous monitoring with annual reporting cycles. The key is establishing a rhythm that maintains compliance while supporting continuous improvement.
What are the core components required for an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
An effective Information Security Management System (ISMS) requires several essential components: documented policies and procedures, comprehensive risk assessment processes, security control implementation, employee training and awareness programs, incident response capabilities, and continuous monitoring and improvement mechanisms. The ISMS should also include regular management reviews, internal audits, and corrective action procedures to ensure ongoing effectiveness and alignment with business objectives.
How do small businesses implement global security standards effectively without overwhelming resources?
Small businesses can start with risk assessment frameworks to prioritize the most critical security controls first. Many standards offer scaled approaches – for example, ISO 27001 allows organizations to scope their ISMS to specific business areas initially. Cloud-based GRC platforms like Secureframe or OneTrust provide automated compliance tools designed for smaller organizations. The key is focusing on foundational controls that provide both security benefits and compliance value, then gradually expanding coverage as resources allow.
What role does employee training play in maintaining compliance with information security standards?
Information security training requirements are fundamental to standards compliance because human error remains a leading cause of security incidents. Most standards require regular awareness training, with specific requirements varying by framework. For example, PCI DSS requires annual security awareness training for all personnel, while GDPR mandates privacy training for data processors. Effective training programs should be tailored to job roles, updated regularly to address emerging threats, and measured through testing and behavioral assessments to ensure effectiveness.
Sources: